 What is Slub Yarn? Slub yarn refers to yarn that has been purposely spun with slubs (thicker sections along the yarn) while it was once ...
What is Slub Yarn? Slub yarn refers to yarn that has been purposely spun with slubs (thicker sections along the yarn) while it was once ...
শুক্রবার, ৬ সেপ্টেম্বর, ২০১৯
সোমবার, ১ এপ্রিল, ২০১৯
How to Calculate Fabric Consumption and Costing for 1 Dozen Trousers
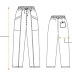 Introduction: Fabric consumption for making a trouser is an important task for garments merchandiser. When a buying house get an order f...
Introduction: Fabric consumption for making a trouser is an important task for garments merchandiser. When a buying house get an order f...
বৃহস্পতিবার, ২৮ মার্চ, ২০১৯
Formulating equations for calculating of circular weft knitted fabric
 Formulating equations for calculating of circular weft knitted fabric Introduction: Fabrics are produced mainly by knitting technique...
Formulating equations for calculating of circular weft knitted fabric Introduction: Fabrics are produced mainly by knitting technique...
মঙ্গলবার, ২৬ মার্চ, ২০১৯
Knit Fabric Consumption Formula, Ahk Fabrics, A trusted fabric supply
 Knit Fabric Consumption Formula, Ahk Fabrics, A trusted fabric supply Introduction: It is very important task for garment merchandise...
Knit Fabric Consumption Formula, Ahk Fabrics, A trusted fabric supply Introduction: It is very important task for garment merchandise...
সিংগেল জার্সি ১৬০ জিএসএম, Ahk Fabrics, A trusted fabric supplier
 সিংগেল জার্সি ১৬০ জিএসএম, Ahk Fabrics, A trusted fabric supplier সিংগেল জার্সি ১৬০ জিএসএম এর সুতি কাপড় তৈরিতে কত কাউন্টের সুতা ব্যবহৃত...
সিংগেল জার্সি ১৬০ জিএসএম, Ahk Fabrics, A trusted fabric supplier সিংগেল জার্সি ১৬০ জিএসএম এর সুতি কাপড় তৈরিতে কত কাউন্টের সুতা ব্যবহৃত...
সোমবার, ২৫ মার্চ, ২০১৯
Merchandiser Job Description in Garments - Ahk Fabrics, A trusted fabric supplier
 Merchandiser Job Description in Garments, Ahk Fabrics, A trusted fabric supplier In garments sector, merchandising is an important depa...
Merchandiser Job Description in Garments, Ahk Fabrics, A trusted fabric supplier In garments sector, merchandising is an important depa...
শনিবার, ২৩ মার্চ, ২০১৯
Eco-Friendly Fibers and Organic Fibers - Ahk Fabrics A Trusted Fabrics Supplier
 Eco-Friendly Fibers and Organic Fibers - Ahk Fabrics A Trusted Fabrics Supplier All natural fibres are not Eco-friendly Fibers Natura...
Eco-Friendly Fibers and Organic Fibers - Ahk Fabrics A Trusted Fabrics Supplier All natural fibres are not Eco-friendly Fibers Natura...
